The Classification and Performance Parameters of Check Valves
A check valve is a valve that has a circular disc as the opening and closing part and blocks the backflow of the medium by its own weight and the pressure of the medium. It belongs to the category of automatic valves, also known as non-return valves, one-way valves, return valves or isolation valves.
Check valve is to allow the medium to flow in one direction only and prevent it from flowing in the opposite direction. Usually, this type of valve works automatically. Under the pressure of the fluid flowing in one direction, the disc opens; when the fluid flows in the opposite direction, the fluid pressure and the deadweight of the disc cause the disc to act on the valve seat, thereby cutting off the flow.
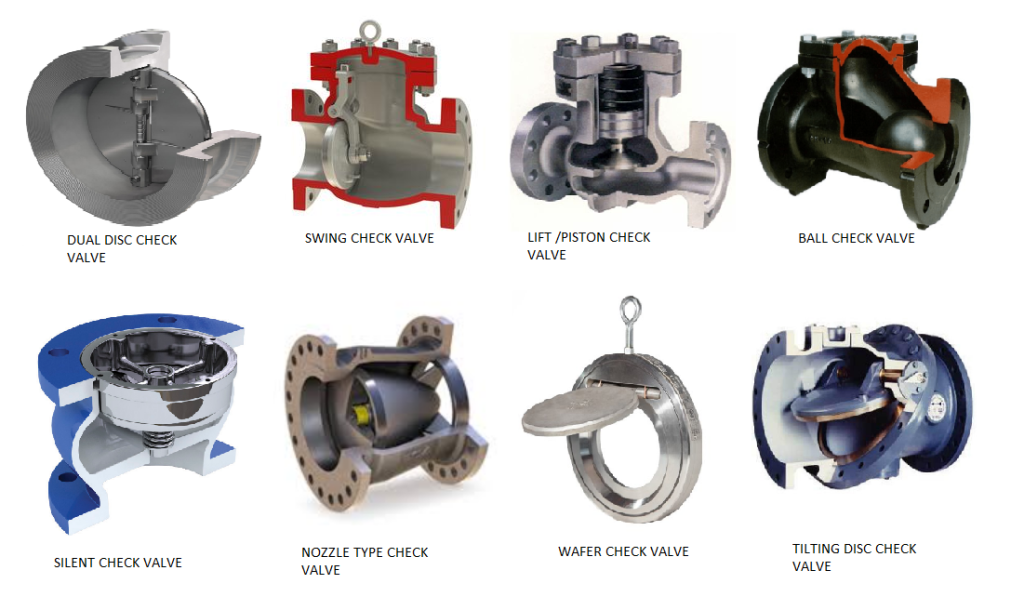

First, classification of check valves.
Ⅰ.By structure
Based on the structure, it can be divided into three types:
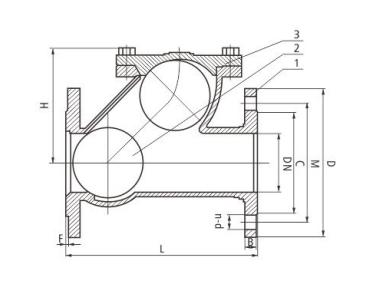
- Lift check valves are divided into vertical and horizontal types.
- Swing check valves are divided into single-flap, double-flap and multi-flap types.
- Butterfly check valves are straight-through.
In terms of connection, the above check valves can be divided into four types: threaded connection, flange connection, welding connection and clamp connection.
Ⅱ.By material
- Cast iron check valve
- Brass check valve
- Stainless steel check valve
- Carbon steel check valve
- Forged steel check valve
Ⅲ.By function
- DRVZ silent check valve
- DRVG silent check valve
- NRVR silent check valve
- SFCV rubber flap check valve
- DDCV double flap check valve
Second, performance parameters of check valves.
Let’s have a general idea about this by comparing in the table:
| Body Material | Nominal pressure (MPa) | Operating temperature (℃) | Applicable media | |
| Carbon Steel | 1.6-6.4 | ≤425 | water, Oil, Steam | |
| 10.0-16.0 | ≤450 | |||
| Stainless teel | P | 1.6-16.0 | ≤200 | Nitric Acid |
| R | 1.6-16.0 | ≤200 | Acetic Acid | |
| Chrome Nickel Titanium Steel | PI | 1.6-6.4 | ≤550 | Petroleum and Petroleum products |
| Chrome-molybdenum Steel | 1.6-16.0 | ≤550 | Oil | |
| Nominal Pressure | Nominal Diameter | Main Connection Dimensions | Outline Dimensions | ||||||||
| PN | DN | L | D | D 1 | D 2 | D 6 | b | f | f 1 | Z-φd | H |
| 1.6MPa | 40 | 200 | 145 | 110 | 85 | – | 16 | 2 | – | 4-18 | 95 |
| 50 | 230 | 160 | 125 | 100 | – | 16 | 2 | – | 4-18 | 105 | |
| 65 | 290 | 180 | 140 | 120 | – | 18 | 2 | – | 4-18 | 120 | |
| 80 | 310 | 195 | 165 | 135 | – | 20 | 3 | – | 8-18 | 130 | |
| 100 | 350 | 215 | 180 | 155 | – | 20 | 3 | – | 8-18 | 140 | |
| 125 | 400 | 245 | 210 | 185 | – | 22 | 3 | – | 8-12 | 155 | |
| 150 | 480 | 280 | 240 | 210 | – | 24 | 3 | – | 8-23 | 180 | |
| 200 | 600 | 335 | 295 | 265 | – | 26 | 3 | – | 12-23 | 215 | |




![[rank_math_breadcrumb]](https://wayvalve.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/non-slam-check-valve-768x934.jpg)
