Globe Valve VS Gate Valve
Both gate valves and globe valves are commonly used shut-off valves, mainly for opening or closing pipelines (fully open or fully closed). They have some similarities in appearance, so many people who have little contact with valves tend to confuse the two. However, they differ significantly in terms of working principles, structures, performances, and application scenarios. Understanding the differences between them helps make more appropriate choices in practical applications.
Ⅰ.Globe valve vs gate valve: design and performance.
1. Different structures.
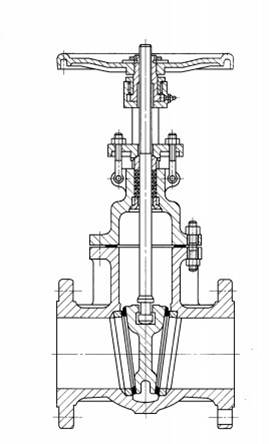
The structure of a gate valve is more complex than that of a globe valve. In appearance, for the same diameter, a gate valve is taller and shorter than a globe valve. In particular, a rising stem gate valve requires more vertical space. Gate valves are divided into rising stem and non-rising stem types, while globe valves have no such distinction.
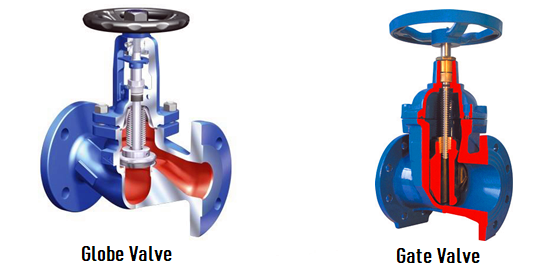
- Gate Valve: It is mainly composed of a valve body, bonnet, stem, gate, valve seat, sealing packing, and driving device. When opening or closing, the gate moves up and down, and the flow path is on a horizontal line.
- Globe Valve: It is mainly composed of a valve body, bonnet, stem, valve disc, valve seat, sealing packing, driving device, etc. When opening or closing, the valve disc moves up and down, and the water flow usually enters from the lower and exits from the upper.
2. Difference in working principle and performance.
The differences of working principles and resulted performance between globe valves and gate valves mainly lie in the following aspects:
Handwheel status when operating.
- When a globe valve opens or closes, the handwheel rotates and moves up and down together with the valve stem. For a gate valve, turning the handwheel drives the valve stem to move up and down while the handwheel itself remains in place.
Opening degree and performance.
- Gate valves require fully open or fully close, while globe valves do not. Therefore, the opening and closing stroke of the gate valve is large, resulting in a longer operation time. The disc movement stroke of a globe valve is much smaller, and the disc can stop at a certain position during movement for flow regulation. Gate valves can only be used for shut-off.
Flowing direction.
- Globe valves have specified inlet and outlet directions, while gate valves have no such requirements.
3. Difference in sealing surface.
- Gate valve: It achieves sealing by pressing the side of the gate against the valve seat. During the opening and closing , there is friction between the gate and the valve seat, which is prone to scuffing. The tightness when closed is slightly poorer than that of globe valves, especially for media containing solid particles or after wear. The sealing performance of parallel dual gate valves is slightly better than that of wedged single gate valves.
- Globe valve: Sealing is achieved by pressing the bottom surface of the valve disc against the valve seat. The contact area between the valve disc and the valve seat is small, and the stroke is short (usually only requiring a 90° rotation or fewer turns to fully close), enabling quicker and tighter closing. The sealing surface is relatively less prone to scuffing, and the sealing performance is generally better than that of gate valves, making it particularly suitable for occasions requiring zero leakage.
4. Different fluid resistance.
- Gate valve: It has very little resistance to the fluid and can be opened and closed flexibly.
- Globe valve: Due to the tortuous channel inside the valve body, the fluid resistance is relatively large.
Ⅱ.Globe valve vs gate valve : application scenarios.
- Globe valves can block the inflow of the medium or regulate its flow rate. They are typically used when the system requires adjustment or throttling.
- Gate valves are used to cut off the medium. When fully open, the entire flow path is straight through. They are generally suitable for working conditions where frequent opening and closing is not required and the gate plate needs to be kept fully open or fully closed. They are not suitable for regulation or throttling.
Ⅲ. Gate valve vs globe valve: pros and cons.
- Gate Valve: The advantages lie in its low flow resistance and easy opening and closing torque; but it should be noted that its sealing performance is relatively poor, and it is not suitable for flow regulation.
- Globe Valve: The advantages include good sealing performance and strong regulating performance; however, it has a relatively large flow resistance, and the opening and closing torque is also quite large.
Ⅳ. Gate valve vs globe valve: maintenance.
- Gate Valve:The structure is relatively simple. However, if the sealing surface of the valve seat is damaged, online repair is usually difficult and often requires removing the valve from the pipeline. Parallel double-disc designs can compensate for wear through wedge blocks.
- Globe Valve:It is relatively easier to repair or replace the sealing surfaces of the valve seat and disc if damaged (especially in designs with removable valve seats). The valve stem packing gland is typically located on the upstream side of the medium, making maintenance more convenient.
Ⅴ. Summary in table.
globe valve vs gate valve: comparison table.
| Characteristics | Gate Valve | Globe Valve |
|---|---|---|
| Working Principle | Gate moves vertically, straight flow path | Disc moves vertically, “S”-shaped flow path |
| Flow Resistance | Extremely low (similar to straight pipe when fully open) | Relatively high (even when fully open) |
| Flow Direction | Bidirectional, no strict installation direction requirement | Unidirectional, must be installed according to arrow (inlet at bottom, outlet at top) |
| Sealing Performance | Good, slightly inferior to globe valves | Better, tighter sealing |
| Opening/Closing Stroke | Long, slow operation | Short, fast operation |
| Flow Regulation | Not suitable (prone to vibration and wear) | Suitable (for rough adjustment) |
| Main Applications | On/off applications, low flow resistance | Shut-off/regulation, high sealing requirements |
| Maintenance | Relatively difficult | Relatively easy |
In conclusion, globe valves and gate valves differ in structure, working principle, and application scenarios. The selection of an appropriate type should be based on specific working conditions and usage requirements to ensure the safe and stable operation of the system.