What is a Gate Valve, and its Applications.
What is a gate valve?
A gate valve is a crucial type of valve in the fluid control field. Here is an introduction to it:
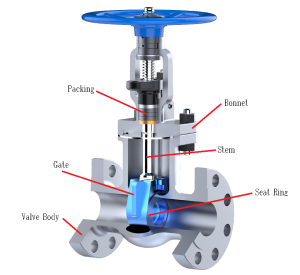
1.Structure
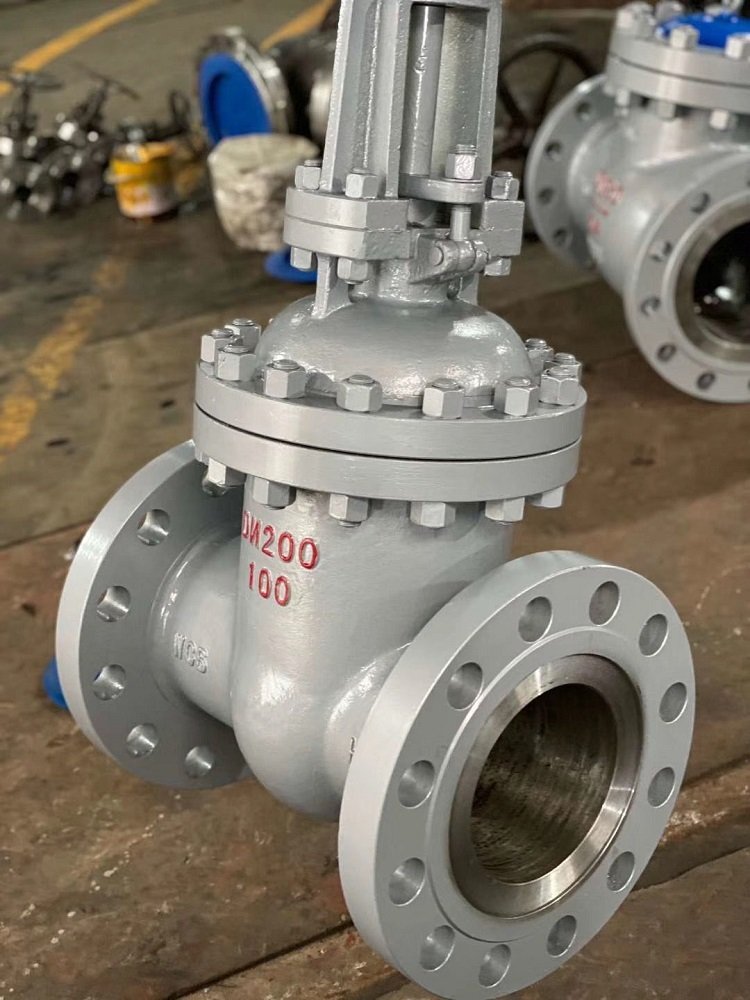
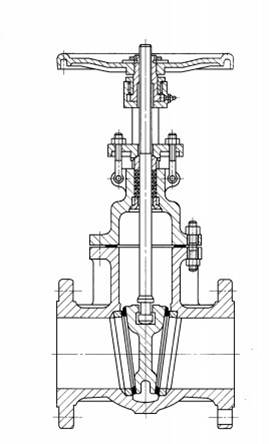
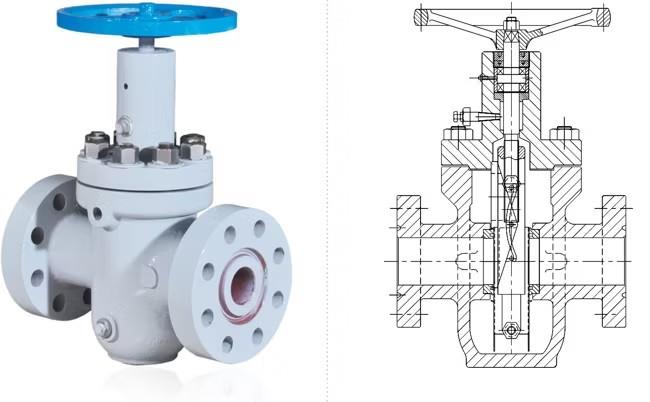
Valve body: It is the main part of the gate valve, which is used to connect pipes and accommodate other components. Usually, it is made of materials like cast iron, cast steel, and stainless steel to withstand different pressures and media.
Bonnet: Installed on the valve body, it is used to enclose the internal space of the valve body, protect internal parts, and provide interfaces for installation and maintenance.
Stem: Connects the gate and the drive device, transmitting the driving force to move the gate up and down to open and close the valve. It requires high strength and wear resistance.
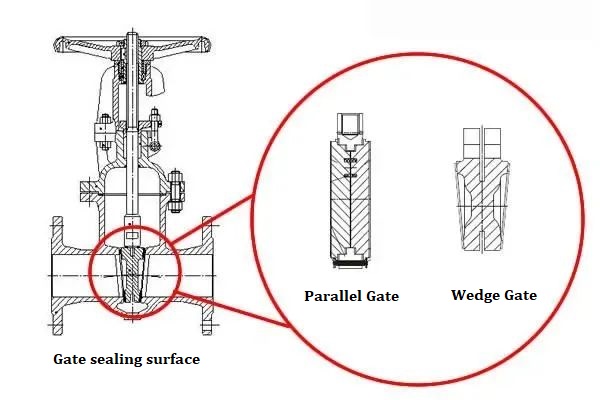
Gate: It is the key opening and closing component of the gate valve. Its moving direction is perpendicular to the fluid direction. It controls the on-off of the fluid through cooperation with the valve seat. The gate can be made in various forms, such as solid and flexible gates.
Seat ring: Located inside the valve body, it fits tightly with the gate to form a sealing surface and prevent fluid leakage. The seat ring material needs to have good sealing performance and wear resistance.
Packing: Fills the gap between the stem and the valve body or bonnet to prevent fluid leakage along the stem. Common packing materials include asbestos, graphite, and PTFE.
2.Working Principle
- Opening: When opening the gate valve, turn the handwheel or drive device to make the stem move upward, driving the gate to rise gradually. When the gate is completely away from the seat ring, the valve is opened, and the fluid can pass through freely.
- Closing: Reverse the rotation of the handwheel or drive device, and the stem drives the gate to move downward until the gate fits tightly with the seat ring, blocking the fluid from passing through and achieving the closing of the valve.
3.Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages
- Low Flow Resistance: The medium channel inside the valve body is straight, and the medium flows in a straight line, resulting in low flow resistance, which is beneficial to energy saving and improving system efficiency.
- Relatively Easy to Open and Close: Compared with globe valves, the gate moves perpendicular to the direction of the medium flow, so it is more labor-saving to open or close.
- Less Likely to Generate Water Hammer Phenomenon: The long closing time can effectively reduce the occurrence of water hammer, which is beneficial to the safety and stability of the pipeline system.
- Unrestricted Medium Flow Direction: The two sides of the channel are symmetrical, and the medium can flow in either direction, which is convenient for installation and use, and increases the flexibility of pipeline layout.
Disadvantages
- Vulnerable Sealing Surface: The sealing surfaces are prone to erosion and abrasion, which will affect the sealing performance of the valve. Once damaged, the maintenance is relatively difficult and requires professional tools and skills.
- Large Size and Long Opening and Closing Time: The gate valve requires a certain space to open, and the opening and closing operation takes a long time, which may not be suitable for occasions that require quick response.

The applications of gate valves.
There are mainly the following fields:
- Petrochemical Industry: It is used to control the transportation and storage of fluids such as petroleum and natural gas, such as in the pipeline systems of refineries and chemical plants.
- Metallurgical Industry: It is used to control the inlet and outlet of fluids such as gas and hot air under high temperature and pressure, as well as the inlet and outlet of equipment such as heating furnaces and cooling towers.
- Power Industry: It is used in the pipeline systems of steam, water and other media in power plants, such as boiler feed water and steam transmission.
- Water Treatment Industry: It is used in the pipeline systems of water treatment plants and sewage treatment plants to control the transportation, distribution and discharge of water.
- Construction Industry: It is used in the water supply and drainage systems and fire protection systems of buildings to realize the control and distribution of water.