A Comprehensive Interpretation of Pressure Reducing Valves.
What is a pressure reducing valve?
Why we need a pressure reducing valve?
The pressure reducing valve, its abbreviation is PRV, also known as a regulator valve. It is a type of valve that reduces the inlet pressure to a required outlet pressure through adjustment, and relies on the energy of the medium itself to automatically maintain the stability of the outlet pressure. The pressure reducing valves can protect equipment from the impact of excessive pressure, enabling it to operate normally. At the same time, it can save energy and reduce material consumption.
The structural design of the pressure reducing valve usually includes the following main parts:
1. Valve body
It is the outer shell of the pressure reducing valve, made of materials such as cast steel, cast iron, or stainless steel. It has sufficient strength and corrosion resistance to withstand the pressure inside the pipeline. There are channels inside the valve body, allowing the fluid to flow from the inlet to the outlet. Its shape is usually spherical or cylindrical, with a compact structure to adapt to different installation spaces and pipeline layouts.
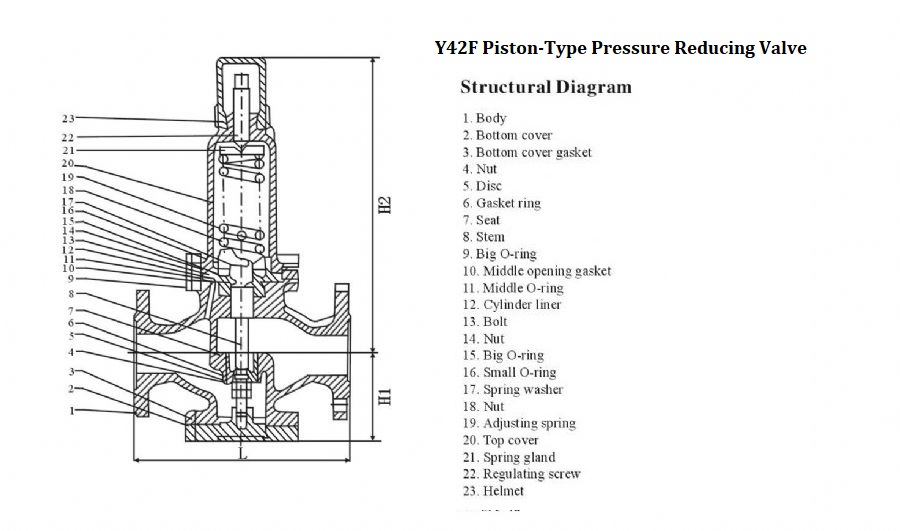
2. Valve seat
It is installed inside the valve body and is a key component that cooperates with the valve core to achieve sealing. It is made of metal or non-metallic materials, such as alloys, polytetrafluoroethylene, etc., and has good wear resistance and corrosion resistance. The surface of the valve seat is finely processed to ensure the sealing performance between it and the valve core. Its shape and size match those of the valve core, and common shapes include conical and spherical.
3. Valve core
It is the core component of the pressure reducing valve, used to regulate the pressure and flow rate of the fluid. The valve core has various structural forms, and common ones include piston type, diaphragm type, spring diaphragm type, etc. The piston-type valve core controls the opening degree of the valve by moving up and down in the valve body; the diaphragm-type valve core uses the deformation of the diaphragm to drive the movement of the valve core; the spring diaphragm-type valve core combines the functions of the spring and the diaphragm, making the movement of the valve core more sensitive and stable.
4. Spring
It is used to provide the force for closing the valve core, keeping the valve core closed when there is no pressure or the pressure is low, and assisting the valve core in regulation when the pressure changes. The stiffness and preload of the spring are designed according to the working pressure and flow requirements. It is made of high-quality spring steel and has good elasticity and fatigue life.
5. Adjustment mechanism.
It consists of components such as adjustment bolts, nuts, and handwheels, and is used to manually adjust the set pressure of the pressure reducing valve. By rotating the adjustment bolts, the preload of the spring is changed, thereby adjusting the opening pressure and flow rate of the valve core. The design of the adjustment mechanism should be easy to operate and accurately adjust, and at the same time have good stability and reliability.
6. Inlet and outlet connection parts
It includes connection methods such as flanges, threads, and welding, and is used to connect the pressure reducing valve to the pipeline system. The size and specifications of the connection parts should match those of the pipeline system to ensure the tightness and sealing performance of the installation. In the design, the strength and stiffness of the connection parts also need to be considered to withstand the pressure and vibration inside the pipeline.
7. Pressure gauge interface
The pressure reducing valve is equipped with a pressure gauge interface for installing a pressure gauge to monitor the pressure at the inlet and outlet in real time. The position and size of the pressure gauge interface should be convenient for installation and reading, and it uses a standard threaded interface that matches commonly used pressure gauges.
Types of pressure reducing valve.
The pressure reducing valve changes the throttling area to regulate the flow rate and kinetic energy of the fluid, thereby causing different pressure losses and achieving the purpose of reducing pressure. Specifically, when the fluid passes through the pressure reducing valve, the throttling element (such as the valve core or valve disc) inside the valve will change the cross-sectional area of the flow channel, resulting in changes in the fluid flow rate and kinetic energy, and thus reducing the pressure. At the same time, relying on the adjustment of the control and regulation system, the fluctuation of the pressure behind the valve is balanced with the spring force (or other adjustment force), so that the pressure behind the valve remains constant within a certain error range.
Pressure regulating valves have a wide variety of classifications. Understanding different classification methods can help people quickly and accurately select suitable valves.
What is the classifications of pressure reducing valves?
From different ways, pressure reducing valves are classified as follows:
Classification by structure:
- Diaphragm-type: It uses the deformation of the diaphragm to regulate the pressure. Its structure is simple and compact, but the durability of the diaphragm is average, and it is suitable for medium and low flow scenarios.
- Spring diaphragm-type: It combines the functions of the spring and the diaphragm to improve the stability and adjustment accuracy of the pressure reducing valve, and is suitable for systems with medium pressure and flow.
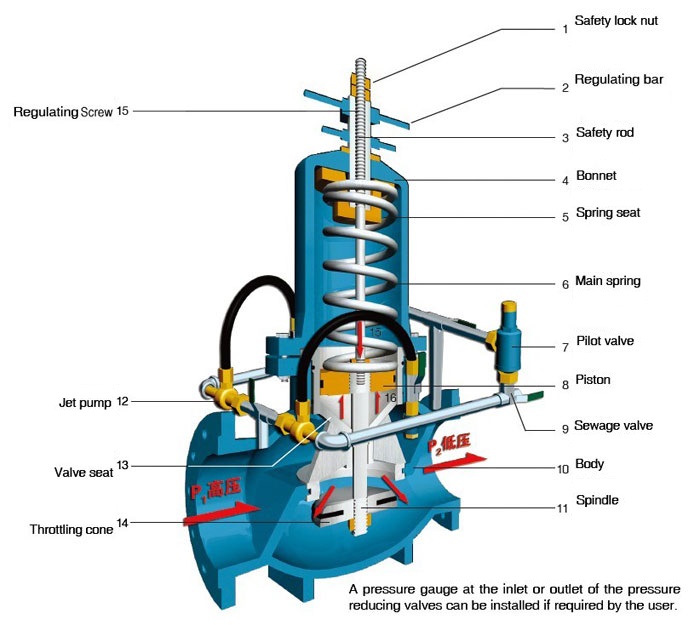
- Piston-type: It regulates the pressure through the movement of the piston. It has high working reliability, can withstand large pressure and flow fluctuations, and is often used in occasions with high pressure, large flow, and high-precision requirements, such as industrial pipelines and hydraulic systems of large equipment.
- Lever-type: It uses the lever principle to convert the change in the input pressure into the displacement of the valve core and control the outlet pressure. Its adjustment accuracy is moderate, and it has a large volume, but it has strong anti-pollution ability and is suitable for occasions with low precision requirements and media containing impurities.
- Bellows-type: It uses the bellows as the sensing element, and its deformation is related to the pressure change, driving the valve core to act. This type of pressure reducing valve has good sealing performance and corrosion resistance and is suitable for environments with high sealing requirements and corrosive media.
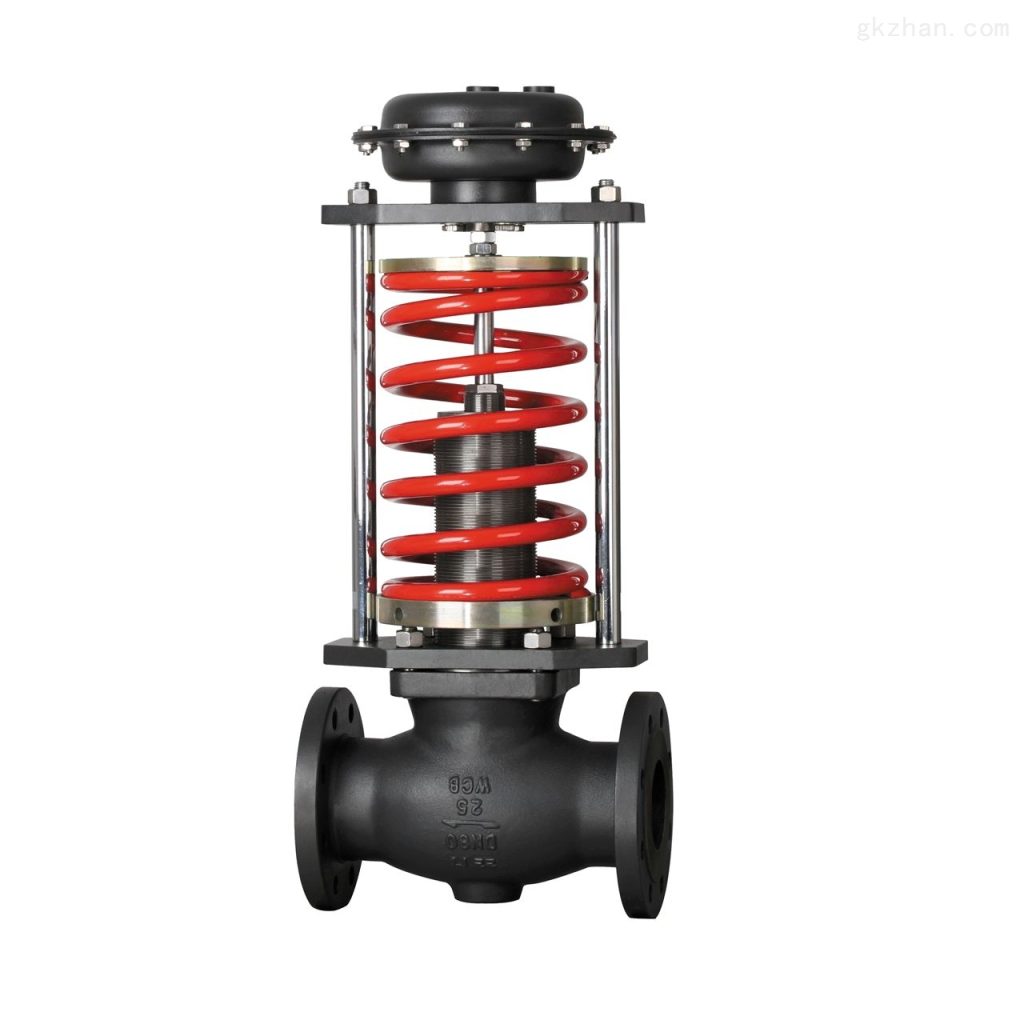



Classification by pressure reduction principle:
- Proportional pressure reducing valve: There is a stable proportional relationship between the inlet pressure and the outlet pressure.
- Adjustable pressure reducing valve: The outlet pressure can be adjusted.
- Stable pressure reducing valve: The outlet pressure remains relatively stable and does not change with the inlet pressure and flow rate.
- Differential pressure reducing valve: A pressure reducing valve in which the dynamic pressure reduction difference between the inlet and outlet remains relatively stable.
Classification by action mode:
- Direct acting type: It directly controls the movement of the valve disc by using the change in the outlet pressure;
- Pilot operated type: It consists of a main valve and a pilot valve, and the change in the outlet pressure controls the action of the main valve through the amplification of the pilot valve.
- Combined type: A pressure reducing valve in which two-stage series pressure reducing devices are combined into one, also known as a series pressure reducing valve.
Classification by the number of valve seats:
- Single-seat: It has only one valve seat, with a simple structure but a limited adjustment range.
- Double-seat: It has two valve seats, with a wider adjustment range and is suitable for complex working conditions.
Classification by the position of the valve disc:
- Positive acting pressure reducing valve: The valve disc moves in the closing direction under the action of pressure.
- Reverse acting pressure reducing valve: The valve disc moves in the opening direction under the action of pressure.
Classification by purpose:
It can be divided into gas pressure reducing valves, liquid pressure reducing valves, steam pressure reducing valves, etc.
The pressure reducing valves for different purposes will vary in structure and material selection to adapt to the characteristics and working conditions of different fluids.
Performance parameters and selection of pressure reducing valves.
performance parameters to be considered.
The performance parameters of the pressure reducing valve mainly include the inlet pressure range, outlet pressure range, maximum flow rate, adjustment accuracy, etc. When selecting a pressure reducing valve, it is necessary to comprehensively consider these parameters according to the specific application scenarios and requirements to ensure the selection of a suitable product.
Application fields of the pressure reducing valve.
The pressure reducing valve is widely used in various industrial and civil fields, such as:
- Energy industry: Such as in the transportation channels of petroleum, natural gas, and coal gas, it is used to reduce the internal pressure of the system and ensure the safe and stable operation of pipeline equipment.
- Chemical industry: It controls the pressure of liquids or gases to ensure the reliable operation of equipment and systems and avoid dangerous situations caused by excessive pressure.
- Gas supply system: It controls the pressure stability in places such as indoor drinking water, heating gas supply, and industrial gas use.
- Thermal system: It controls the supply pressure of hot water to ensure the smooth and safe operation of the entire system.
- Water supply and drainage system: Such as in urban water supply pipelines, sewage treatment systems, etc., it maintains the normal operation of pipelines and equipment by regulating the pressure.
- Aerospace field: It is used to control the internal pressure of aircraft and spacecraft to ensure the safety of passengers and crew members.
- Other fields: It is also widely used in industries such as the printing industry, pharmaceutical industry, and automobile manufacturing.

Installation and maintenance of pressure reducing valves.
Installation Requirements:
- The pressure reducing valve should generally be installed on a horizontal pipeline for convenient pressure adjustment and maintenance.
- During installation, it is necessary to strictly maintain the same direction as the fluid flow according to the arrow direction on the valve body.
- If the water quality is not clean or contains impurities, a filter must be installed at the upstream inlet of the pressure reducing valve.
- In order to prevent the pressure behind the valve from exceeding the allowable value, another pressure reducing valve or safety valve should be installed at a distance of not less than a certain distance (such as 4M) from the valve outlet.
Maintenance Requirements:
- Regularly check the sealing performance, action flexibility, and outlet pressure stability of the pressure reducing valve.
- Regularly clean the inside of the pressure reducing valve to remove accumulated impurities and dirt.
- If a fault or performance degradation of the pressure reducing valve is found, it should be repaired or replaced in a timely manner.
Common faults and solutions of pressure reducing valves.
Why the outlet pressure is almost equal to the inlet pressure, and there is no pressure reduction?
Reasons: Burrs or dirt on the main valve core cause jamming, resulting in poor pressure reduction effect; the improper clearance between the main valve core and the valve body hole affects the passage of the fluid; the damping hole or the valve seat hole is blocked, making the pressure reducing valve ineffective.
Solutions: Remove the burrs, clean and repair the valve hole and the valve core to ensure the precision; adjust the clearance to a reasonable range; use a steel wire or compressed air to clean the damping hole, and then reassemble it.
Why the outlet pressure is very low and cannot be increased?
Reasons: The inlet and outlet ports of the pressure reducing valve are connected in reverse, preventing the pressure from being established; the pressure at the inlet port is insufficient; the load of the downstream circuit is too small to form sufficient pressure.
Solutions: Check and correct the connection of the inlet and outlet ports; find out the cause of the low pressure at the inlet port and solve it; install a throttle valve downstream of the pressure reducing valve to increase the pressure.
Why the pressure is unstable, with large fluctuations, and sometimes accompanied by noise?
Reasons: Using the pilot valve interchangeably with the relief valve may lead to similar faults; the pressure reducing valve is used beyond its rated flow capacity; the back pressure at the oil drain port is large; the spring is deformed or has poor stiffness.
Solutions: Refer to the relief valve to troubleshoot the problem; Select a pressure reducing valve of appropriate model and specification; Reduce the back pressure at the oil drain port; Replace the spring with a qualified one.
Why the working pressure rises spontaneously after being set?
(The specific reasons and solutions are not given here, and they can be described according to the actual situation)
Reasons: The clearance between the main valve core and the valve body hole is too large, or the main valve core is severely worn, resulting in an increased leakage amount.
Solutions: Consider replacing the main valve core with a new one, or repair the worn main valve core to reduce the leakage.
In conclusion, the pressure reducing valve is an important fluid control device widely used in multiple fields. By reasonably selecting, correctly installing, and regularly maintaining the pressure reducing valve, the safe and stable operation of the system can be ensured and the work efficiency can be improved.






