What are the differences between pin and pinless butterfly valves?
In industrial fluid control systems, butterfly valves are widely used in petroleum, chemical, power, metallurgy, water treatment and other fields due to their simple structure, small size, light weight, easy operation and low flow resistance. According to the difference in the connection mode between the valve stem and the disc, butterfly valves are mainly divided into pin butterfly valves and pinless butterfly valves. Although both are used to cut off or regulate fluid, they have significant differences in structure, performance, maintenance and applications. A deep understanding of these differences is crucial for the correct selection, installation and maintenance of butterfly valves to ensure the stable and efficient operation of industrial systems.

1. Different structure design.
1.1 Structure of pin butterfly valves.
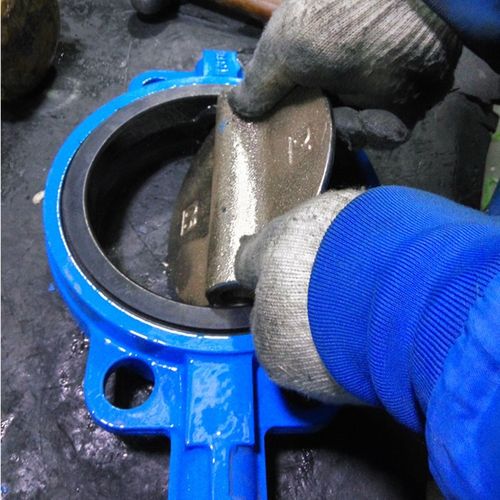
Pin butterfly valves use a pin to connect the valve stem and the disc. The pins are usually made of high-strength metals such as stainless steel or alloy steel to withstand large shear forces and torques during frequent opening and closing. The pin passes through the pin holes in the valve stem and disc, and is fixed by nuts or other locking devices. This connection allows the disc to be stably mounted on the valve stem, and when the valve stem rotates, the disc accurately follows the stem’s movement to open and close the valve.
In addition, pin butterfly valves are equipped with components such as seats, bodies and seals. The seat is usually installed inside the valve body and cooperates with the disc to provide sealing. Seals are installed between the disc and the seat to further improve the valve’s sealing performance. The valve body structure of pin butterfly valves is relatively complex, requiring precise machining of pin holes and other components to ensure the fitting accuracy between parts.
Case of applicaition: In the atmospheric and vacuum distillation unit of a large petrochemical enterprise, the pinned butterfly valves which stems and discs are connected by stainless steel are applied. Under long-term exposure to high temperature, high pressure and highly corrosive media, the pins can still ensure the stable operation of the disc due to their high strength. However, due to the complex stress on the pins over time, some pins showed wear after 3 years of operation. And after timely replacement of the pins, the valves coutinue their stable operations.
1.2 Structure of pinless butterfly valves.
Pinless butterfly valves abandon the traditional pin connection and adopt fastening methods such as collets or slots to connect the valve stem and disc. For the collet connection, the end of the valve stem is designed with a specially shaped collet, and the corresponding position on the disc is machined with a slot. During installation, the collet is inserted into the slot, and the collet and slot are tightly fitted by nuts or other means to connect the valve stem and disc. This connection reduces the number of components (pins) and simplifies the valve structure.
Pinless butterfly valves also have basic components such as seat, body and seal. Since no pin is required, the valve body structure is relatively simple, reducing complex processes such as machining pin holes and lowering manufacturing costs. In addition, pinless butterfly valves focus more on overall strength and stability in design, ensuring reliable operation during work by optimizing the connection between the valve stem and disc.
Case of applicaition: In the grid chamber of a sewage treatment plant, pinless butterfly valves with collet connections effectively avoid the impact of impurities in the sewage on pins. During 5 years of continuous operation, only the seals were replaced twice, and the connection between the valve stem and disc remained stable throughout, demonstrating good reliability.
1.3 The impact of structure differences.
- Pin butterfly valves: The pin connection allows for relatively convenient installation and removal of the disc–simply remove the pin for maintenance or replacement. However, pins, as independent components, carry risks of wear and loosening, requiring regular inspection and maintenance.
- Pinless butterfly valves: The connection structure is more compact, reducing the possibility of failures caused by component loosening and improving valve reliability. However, maintaining or replacing the disc is more complex, requiring special tools and techniques.
2. Differences in sealing performance.
2.1 Sealing performance of pin butterfly valves.
When closed, the disc of a pin butterfly valve can be accurately positioned on the seat via the pin, achieving good sealing. The pin connection ensures the stability of the disc during movement, allowing it to fit tightly with the seat and effectively prevent medium leakage. In addition, pin butterfly valves typically use high-quality sealing materials such as rubber or PTFE to further enhance sealing performance. In applications with extremely high sealing requirements, pin butterfly valves can adopt a dual-sealing structure (combining soft and hard seals) to ensure reliable sealing under various working conditions.
Case of applicaition: In a natural gas transmission pipeline project, pin butterfly valves were used at critical nodes. With a dual-sealing structure and the disc accurately positioned by pins to fit tightly with the seat, these valves effectively prevented natural gas leakage. Even under significant pipeline pressure fluctuations, the valves maintained good sealing performance, ensuring the safe transportation of natural gas.
2.2 Sealing performance of pinless butterfly valves.
Pinless butterfly valves can also achieve good sealing performance through special connection structures and reasonable sealing designs. The pinless structure allows the disc to more flexibly adapt to the shape of the seat when closed – for irregular or slightly deformed seats, pinless butterfly valves can adjust via their own structure to achieve better sealing. In addition, pinless butterfly valves offer diverse sealing material options, allowing suitable materials to be selected based on different media and working conditions to meet various sealing requirements.
Case of applicaition: A pharmaceutical factory adopted pinless butterfly valves in its liquid medicine transportation system. Despite slight deformation of the valve seats after long-term use, the pinless butterfly valves maintained good sealing performance by flexibly adapting the disc to the seats, avoiding liquid medicine leakage and its impact on product quality.
2.3 The impact of sealing performance differences.
- General conditions: Both types meet sealing requirements under normal conditions.
- Special conditions:
- Pin valves: In high-temperature, high-pressure or highly corrosive environments, thermal expansion or corrosion of pin may affect sealing performance.
- Pinless valves: With a simpler structure and no pin-related issues, they exhibit more stable sealing in special conditions. However, for applications requiring extremely high sealing precision, the precise positioning of pin valves may be more preferable.
3. Differences in flow capacity.
3.1 Flow capacity of pin butterfly valves.
With reasonable design, the disc opening angle and flow channel of pin butterfly valves can meet most working conditions, allowing smooth medium flow. However, the presence of pins can slightly obstruct medium flow. When the medium contains impurities or particles, accumulation may occur around the pins, affecting flow capacity. Improper pin installation or loosening may also cause disc wobbling during opening/closing, further disrupting flow.
Case of applicaition: In a mine concentrator’s slurry pipeline, pin butterfly valves were used. Due to the large number of ore particles in the slurry, particle accumulation around the pins occurred after some time, lead ing to flow capacity decrease and pipeline pressure increase. The enterprise had to regularly clean and maintain the valves, which resulted in increasing operation costs.
3.2 Flow capacity of pinless butterfly valves.
Pinless butterfly valves have an advantage in flow capacity without the obstruction of pins. For media with impurities or particles, the pinless structure reduces internal accumulation, enabling smoother flow and lower blockage risks. Additionally, the disc moves more smoothly during opening/closing, ensuring better flow stability.
Case of applicaition: The same mine concentrator replaced some production lines with pinless butterfly valves. Slurry flow became smoother, and blockages decreased significantly. The cleaning cycle was extended from monthly to quarterly, greatly improving production efficiency.
3.3 The impact of flow capacity differences.
- Clean media/low flow requirements: flow capacity differences have no much impact on pin butterfly and pinless butterfly valve under these conditions.
- Dirty media/high flow requirements: pinless valves excel by reducing blockage-related system failures and improving operational efficiency.
4. Differences in maintenance.
4.1 Maintenance of pin butterfly valves.
Pin butterfly valves require relatively complex maintenance, including regular checks of pin wear, looseness and seal aging. Pins are prone to wear and deformation under long-term shear forces and torques. Severe wear or looseness can cause disc-stem connection failure, affecting valve operation. Therefore, pins must be regularly inspected and replaced, and the sealing surfaces of the disc and seat must be cleaned and maintained to prevent damage from impurities or corrosion.
Case of applicaition: On the steam pipelines of a thermal power plant, pin butterfly valves were subject to rapid pin wear due to high-temperature and high-pressure steam working condition. The plant implemented a strict maintenance plan: inspecting pins quarterly, replacing them annually, and maintaining sealing surfaces to ensure stable valve operation.
4.2 Maintenance of pinless butterfly Valves.
Pinless butterfly valves are easier to maintain, as they are free of pins (a wearing part). Maintenance focuses on seals and stem lubrication. Regularly inspect the seal wear, replace aging or damaged seals in a timely manner, and lubricate the stem to reduce friction and extend service life. The simple structure reduces maintenance workload and costs.
Case of applicaition: In the secondary water supply system of a residential community, pinless butterfly valves only require annual seal inspections and semi-annual stem lubrication by maintenance personnel – significantly reducing maintenance costs and workload compared to pin valves.
4.3 The impact of maintenance differences.
- Pin valves: Require higher maintenance expertise and costs. Improper maintenance can easily cause valve failures and disrupt system operation.
- Pinless valves: Simplified maintenance reduces technical requirements, costs and downtime, enhancing system reliability and stability.
5. Differences in application scenarios.
5.1 Application scenarios for pin butterfly valves.
Pin butterfly valves are widely used in industrial fields such as petroleum, chemical, power and metallurgy, especially in scenarios requiring high sealing performance and stability:
- Petrochemical industry: Suitable for flammable, explosive, toxic or harmful media (e.g., oil and gas in a refinery’s catalytic cracking unit), where precise positioning and excellent sealing of pin valves are essential to prevent leakage and ensure safety.
- High-temperature/High-pressure systems: Perform well in steam systems, maintaining stability under harsh conditions.

5.2 Application scenarios for pinless butterfly valves.
Pinless butterfly valves are commonly used in sewage treatment, mining, construction and other industries:
- Sewage treatment/minings: Resist blockage from media with impurities or particles (e.g., slurry in mines or sewage in treatment plants).
- High-rise buildings: Their light weight and simple structure make them suitable for water supply/drainage systems, facilitating installation and maintenance while resisting impurity-related blockages.
5.3 The impact of application scenario differences.
Correctly selecting between the two types improves system efficiency, reduces costs and ensures safety. Using the wrong type may lead to frequent failures, higher maintenance costs and even system disruptions.
5.4 Selection guide for pin and pinless butterfly valves.
When selecting between pin and pinless butterfly valves, comprehensively consider the following based on working conditions and system requirements:
- Sealing requirements:
- High precision (e.g., natural gas, pharmaceuticals): Choose pin valves with precise pin positioning and dual-sealing structures.
- Deformable seats (e.g., old pipelines): Choose pinless valves for disc flexibility to adapt to seat shapes.
- Media characteristics:
- Clean media: both types are suitable.
- Dirty media with particles (e.g., slurry, sewage): prioritize pinless valves to reduce blockage risks.
- Maintenance difficulty:
- Professional teams/high budgets: pin valves are acceptable despite complex maintenance.
- Simple maintenance needs: Pinless valves are preferable for reduced workload and costs.
- Space/weight limitations:
- Narrow installation space(e.g., water supply,drainage systems): the advantages of pinless butterfly valves:simple structure and light weight,make it the preferred choice.
- Without space restrictions: cosider all the other factors.
- Working conditions:
- High temperature/pressure/corrosion: pinless valves are more stable due to fewer vulnerable components.
- General conditions: base the choice on sealing and media requirements.
6. Conclusion.
Pin butterfly valves and pinless butterfly valves exhibit significant differences in structural design, sealing performance, flow capacity, maintenance requirements, and application scenarios. In practical applications, it is necessary to comprehensively consider various factors and select the appropriate type of butterfly valve based on specific working conditions.
With continuous technological development, the design and manufacturing technologies for butterfly valves are also evolving. In the future, both pin and pinless butterfly valves will continue to innovate in their respective application fields, providing more reliable support for the development of industrial fluid control systems.






